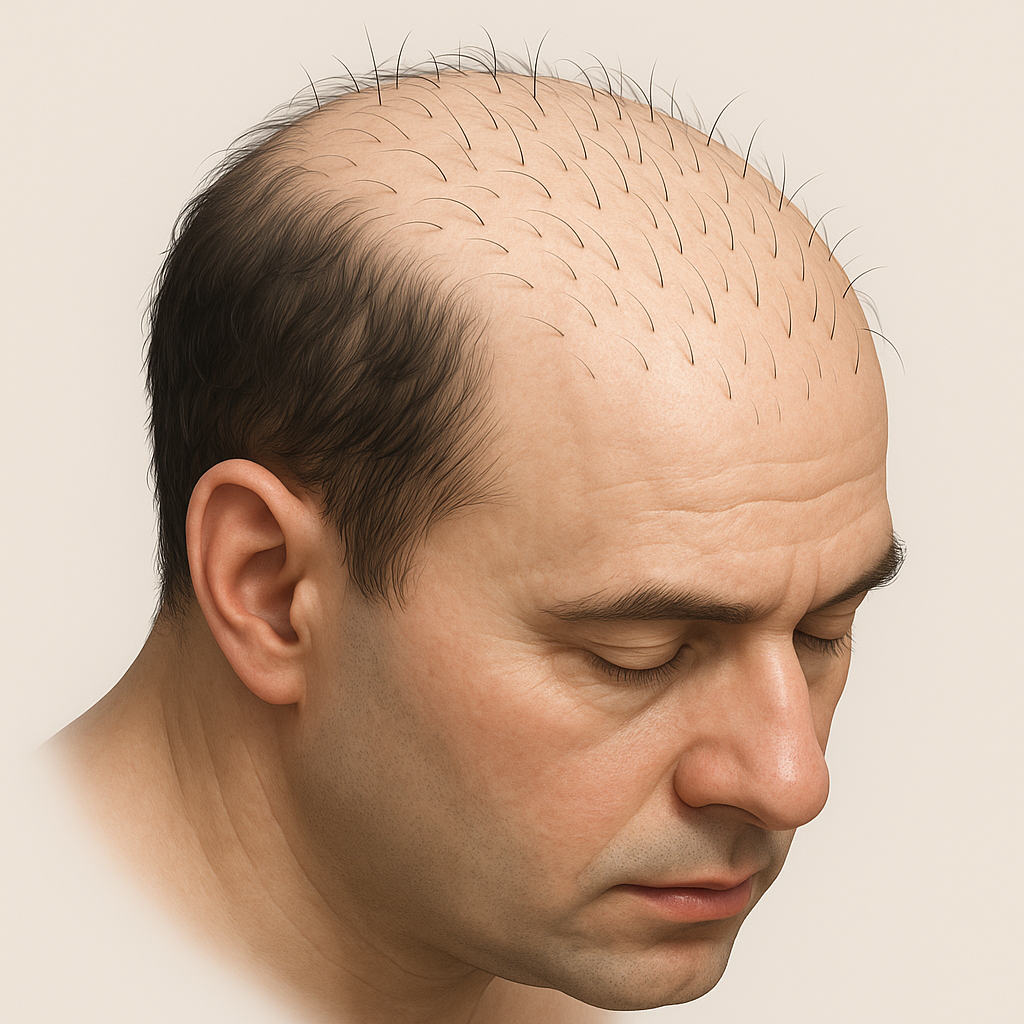
Introduction
Hair fall is the excessive shedding or loss of hair from the scalp or body, which can result from genetic, hormonal, nutritional, medical, or environmental
Cause

1. Hormonal Changes Can Harm Hair
Changes during pregnancy, menopause, thyroid problems, or PCOS can lead to sudden or gradual hair fall.
- Lack of Proper Nutrition
Your hair needs vitamins and minerals like iron, protein, and vitamin D. Poor diet = weak, falling hair.
3. Family History (Genetics)
If your parents or grandparents had hair loss, you might too. It’s a natural pattern for some people.
4. Stress Makes Hair Fall Faster
Too much stress, shock, or illness can make your hair fall out more than usual. Relaxation helps!
5. Bad Hair Habits
Using harsh shampoos, too much heat, or tight hairstyles can damage your hair and make it fall.
6. Side Effects of Medicines
Some medicines, like those for blood pressure, depression, or cancer treatment, may cause hair fall.
7. Aging and Natural Thinning
As you grow older, hair becomes thinner and may fall more. It’s a normal part of aging.
8. Scalp Problems
Infections, dandruff, or skin conditions can damage the scalp and lead to hair loss.
Non-pharmacological treatments for hair loss focus on lifestyle changes, natural remedies, and procedures that help manage or slow down the process of hair shedding. Here are the key approaches:
Treatment
For hair loss related to pattern baldness or alopecia, there are a couple of common medications:
- Minoxidil: This is an over-the-counter topical treatment that you apply to your scalp. It’s commonly used for both men and women and can help promote hair growth and slow hair loss.
- Finasteride: This is a prescription oral medication primarily for men. It works by inhibiting the hormone responsible for hair loss.
Both medication can be effective, but results vary from person to person. It’s best to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment for your specific situation.
1-Topical Medications
Topical corticosteroids
Used for: Alopecia areata
Function: Reduces inflammation and suppresses immune response.
Example: Clobetasol propionate
2-Topical immunotherapy
Used for: Severe alopecia areata
Function: Provokes a mild allergic reaction to stimulate hair growth.
Example: Diphencyprone (DPCP), squaric acid dibutylester (SADBE)
3-Oral Medications
Dutasteride Similar to finasteride, but inhibits both type I and II 5α-reductase enzymes.
Often used off-label for hair loss in men.
Spironolactone
Used for: Female pattern hair loss
Function: Blocks androgen receptors; reduces hair-thinning effects of androgens.
4-Oral corticosteroids
Used for: Severe alopecia areata
Function: Suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation.
Low-dose oral minoxidil
An emerging option when topical minoxidil isn’t effective or causes irritation.
5- Injectable / Biologic Therapies
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy.Autologous platelets are injected into the scalp to stimulate hair follicles.
6-JAK Inhibitors
Used for: Alopecia areata (especially severe cases)
Examples: Tofacitinib, ruxolitinib, baricitinib (baricitinib is FDA-approved for alopecia areata)
Other / Experimental Options
Prostaglandin analogs (e.g., latanoprost, bimatoprost) – originally used for glaucoma, may promote eyelash and scalp hair growth.
Caffeine -based topical formulations.
Ketoconazole shampoo – antifungal with anti-androgenic properties that may help with hair thinning.
1. Diet and Nutrition
Balanced diet rich in vitamins (A, C, D, E), minerals (zinc, iron, biotin), and protein can support hair health.
Iron-rich foods (spinach, lentils) and vitamin D (sunlight, fortified foods) are particularly important for preventing deficiency-related hair loss.
2. Scalp Care
Regular scalp massages with oils like coconut oil, castor oil, or argon oil can increase blood flow to hair follicles, promoting growth .Gentle hair washing and using mild shampoos can avoid damaging the hair.
3. Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to hair shedding, so practices like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or exercise help reduce stress and prevent hair loss related to stress (telogen effluvium).
4. Hair Restoration Procedures
Hair Transplant Surgery involves moving hair follicles from areas with thick growth to areas where hair loss has occurred.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy uses your blood’s growth factors to stimulate hair follicles.
5. Laser Therapy
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) uses red light to stimulate hair follicles, improve blood circulation to the scalp, and promote growth.
6. Essential Oils
Rosemary oil, peppermint oil, and lavender oil have shown potential in promoting hair growth when massaged into the scalp regularly.
7. Hair-Friendly Lifestyle Habits
Avoid tight hairstyles (like ponytails) that put pressure on the hair (traction alopecia).
Limit the use of heat styling tools (straighteners, curling irons) and chemical treatments (dyes, perms) that can damage hair.
8. Alternative Therapies
Acupuncture: Some believe it can stimulate blood flow to the scalp and improve hair growth.
Herbal Supplements: Supplements like saw palmetto or ginseng may offer some benefits in promoting hair health.
These treatments aim to manage hair loss or improve hair health without medications. It’s often best to combine these with professional advice to determine the most effective approach.
Blog Post
1
2
3
4
5
…. View Alll